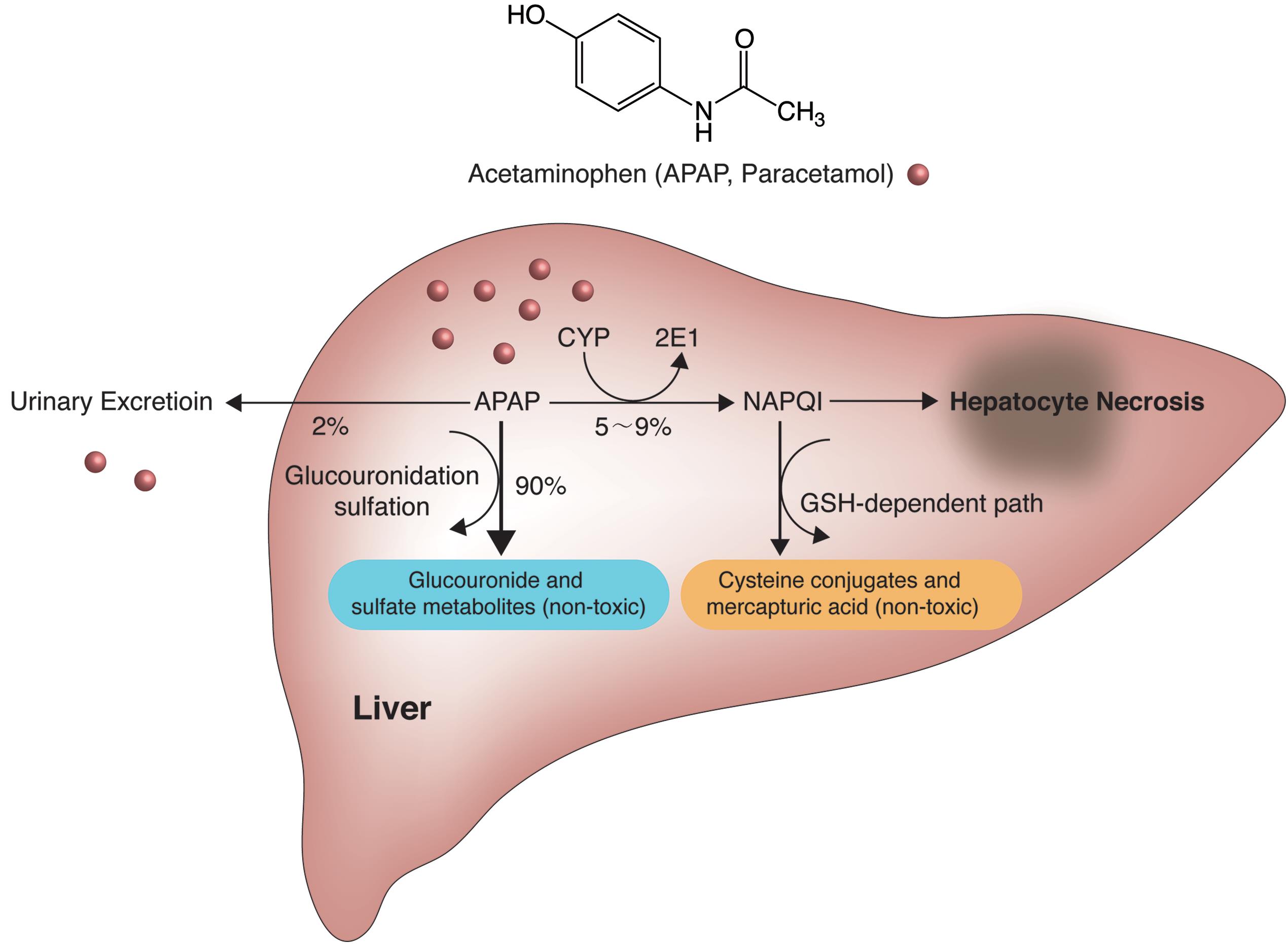
Necrostatin-1 protects against reactive oxygen species (ROS)-induced hepatotoxicity in acetaminophen-induced acute liver failure - ScienceDirect

Role of the inflammasome in acetaminophen-induced liver injury and acute liver failure - Journal of Hepatology
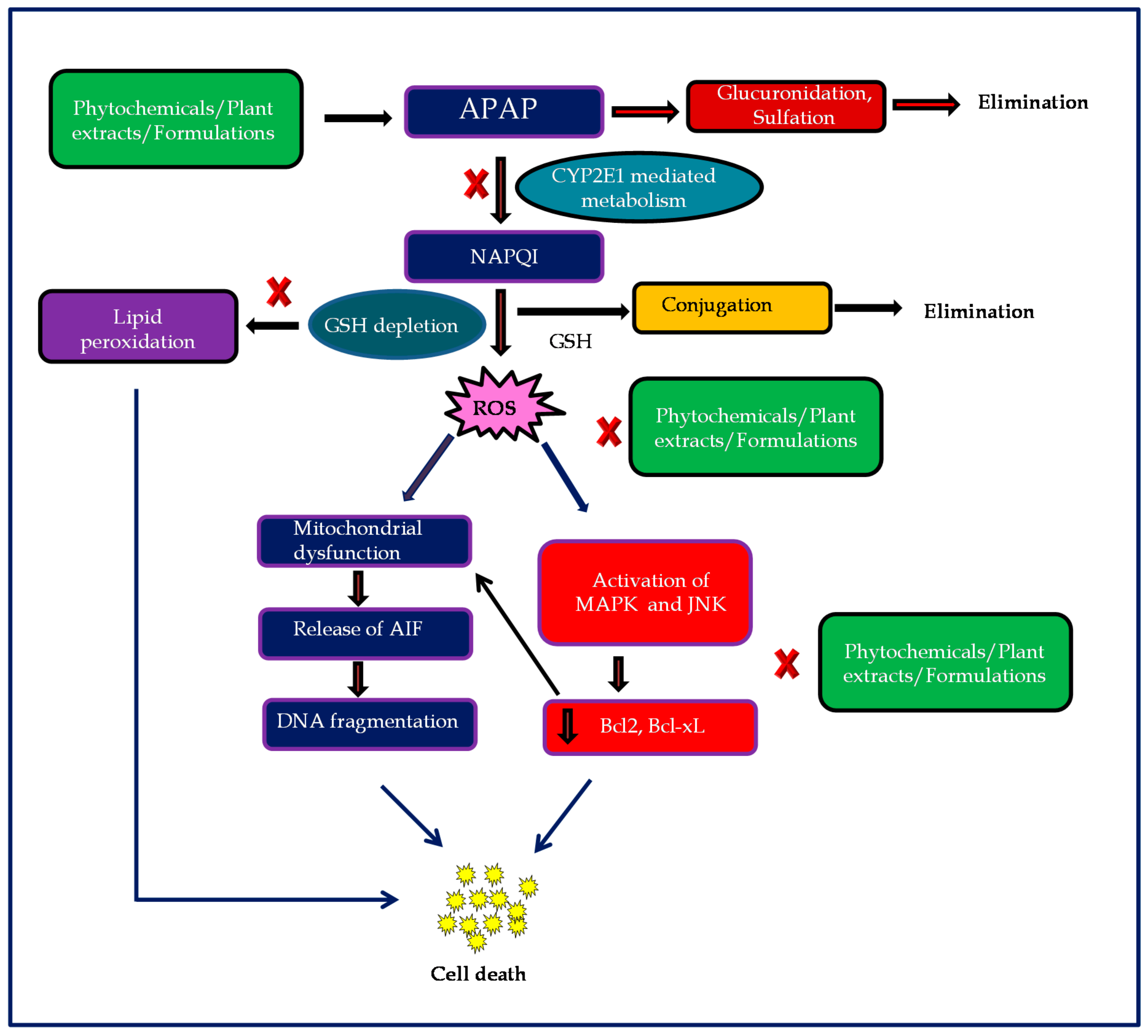
IJMS | Free Full-Text | Therapeutic Potential of Plants and Plant Derived Phytochemicals against Acetaminophen-Induced Liver Injury | HTML

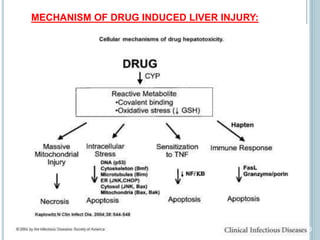
Mechanism of acetaminophen-induced cell death. During conditions of... | Download Scientific Diagram

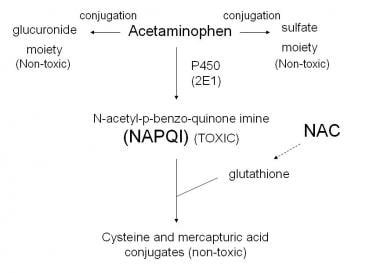
Postulated mechanism of acetaminophen (APAP)-induced hepatotoxicity.... | Download Scientific Diagram

Role of the inflammasome in acetaminophen-induced liver injury and acute liver failure - Journal of Hepatology

Supplemental Materials for Fibrin(ogen) drives repair after acetaminophen-induced liver injury via leukocyte αMβ2 integrin-dependent upregulation of Mmp12 - Journal of Hepatology

Endoplasmic Reticulum Stress-Induced Upregulation of STARD1 Promotes Acetaminophen-Induced Acute Liver Failure - Gastroenterology

Mechanism of acetaminophen-induced cell death. During conditions of... | Download Scientific Diagram

Role and mechanisms of autophagy in acetaminophen‐induced liver injury - Chao - 2018 - Liver International - Wiley Online Library
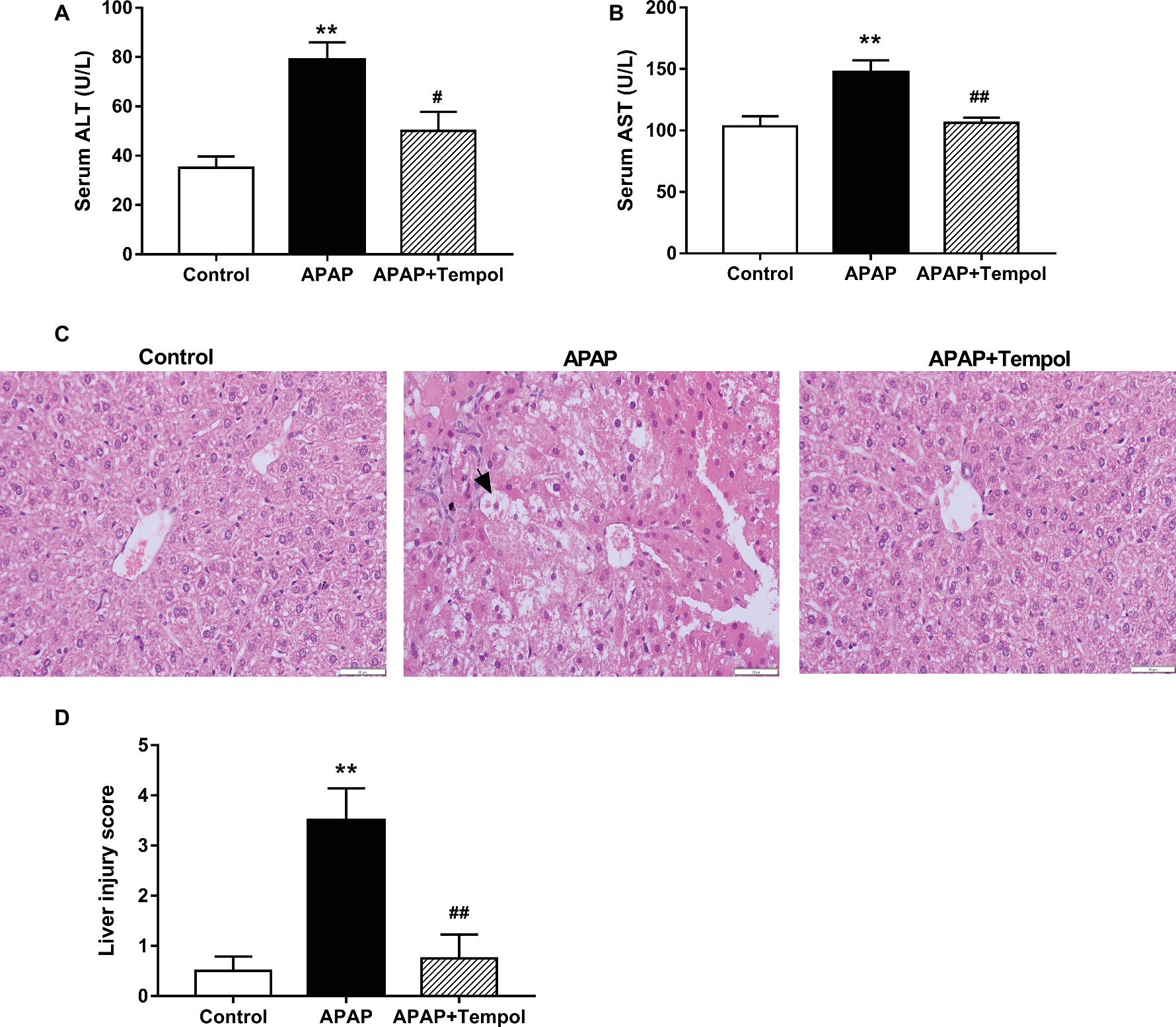
Frontiers | Tempol Protects Against Acetaminophen Induced Acute Hepatotoxicity by Inhibiting Oxidative Stress and Apoptosis | Physiology

Gut Abnormalities: New Insights Into the Pathogenesis of Acetaminophen‐Induced Liver Injury? - Chen - 2019 - Hepatology Communications - Wiley Online Library
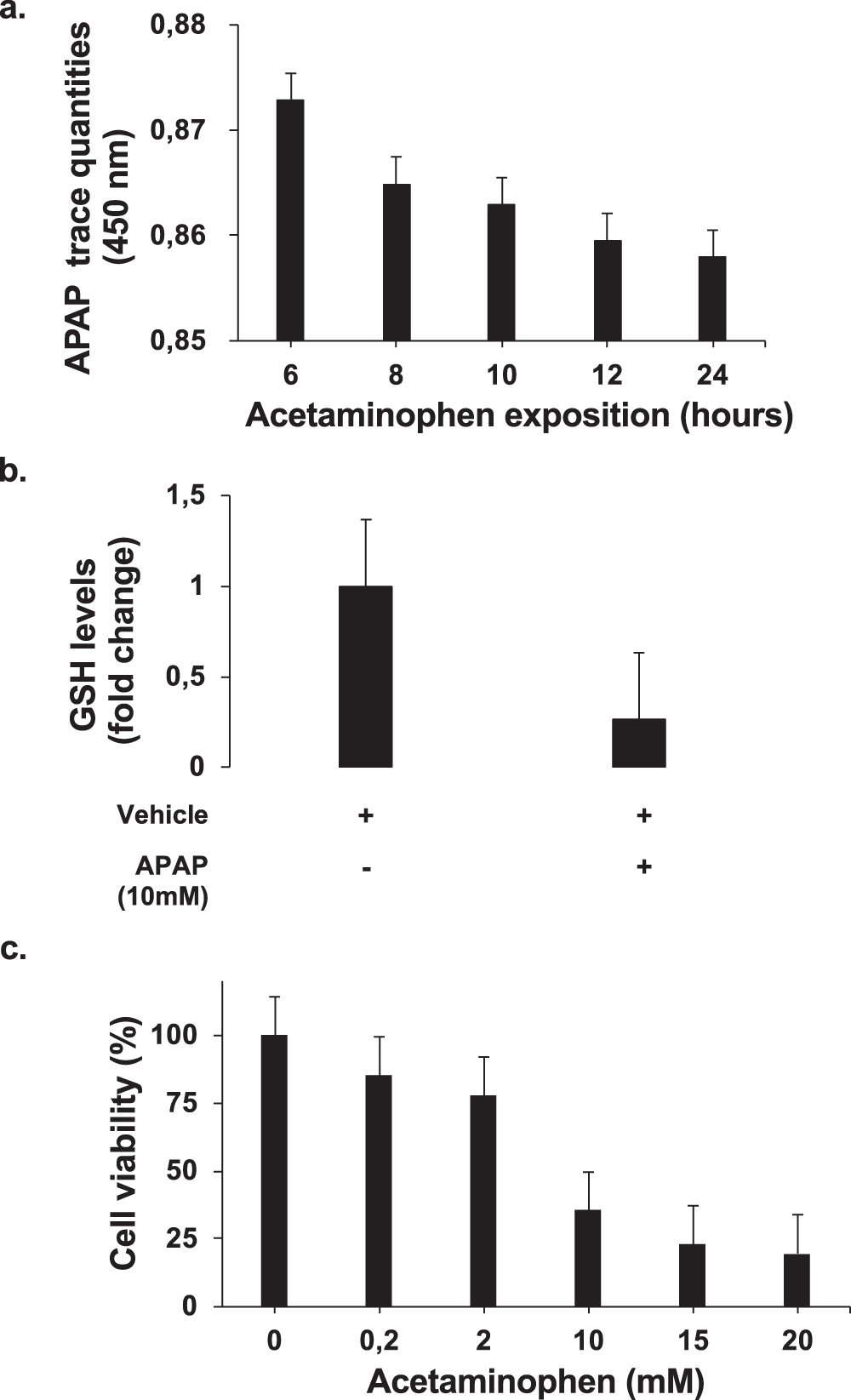
New insights in acetaminophen toxicity: HMGB1 contributes by itself to amplify hepatocyte necrosis in vitro through the TLR4-TRIF-RIPK3 axis | Scientific Reports
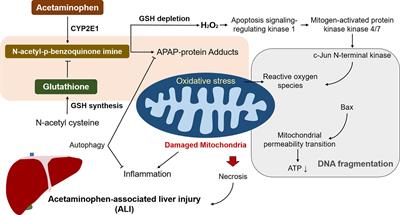
Frontiers | Herbal Therapy for the Treatment of Acetaminophen-Associated Liver Injury: Recent Advances and Future Perspectives | Pharmacology